What Is Some Information That Should Be Found In Big Data Databases?
Big Data: An In-Depth Introductory Guide
Large Data means new opportunities for organizations to create business value — and excerpt it. MongoDB offers products and services that get you to production faster with less risk and endeavor.
Picture show this: Y'all watch a video on YouTube, similar it, and share it with a few friends. Y'all and so purchase groceries and medicine online, and search for absurd places to vacation. You open Netflix and watch your favorite web series. You pay your parents' telephone and electricity bills, and update their details on a health portal to apply for insurance. A friend calls you lot up to like their content on Instagram, and so you log in to your business relationship and post comments on a few of their photos. So, y'all book your flight to your parents' place for adjacent weekend.
With all these transactions, you keep generating data and sharing personal information about yourself and people you are related to—your parents, your friends, your favorite serial, your favorite travel destinations, and more.
As you proceed transacting in diverse means, the magnitude and variety of information grows at a very fast rate. And that's just your data! Imagine the amount of data each of the 4.66 billion agile internet users worldwide produces daily!
This data that is huge in 5olume (size), Variety, and Fiveelocity (speed) is known as big data. In this article, nosotros will explore what big data is and how it is transforming businesses to help them increase revenue and better their business organisation strategies and processes.
What is Big Information?
We saw above that a user can generate data in diverse ways—from the fettle app that you lot use, doctor visits you schedule, or videos you spotter, to the Instagram posts you like, grocery purchases y'all make online, games y'all play, vacations you book—and every transaction that you make (or abolish) generates data. Generally, that data is analyzed by businesses to better sympathize their users and present them with customized content.
Big data is used in near all major industries to streamline operations and reduce overall costs.
For example, big data in healthcare is becoming increasingly important—early detection of diseases, discovery of new drugs, and customized treatment plans for patients are all examples of big data applications in healthcare.
Information technology's a complex and massive undertaking to capture and analyze so much data (for example, data almost thousands of patients). To perform big data analytics, data scientists require big data tools, equally traditional tools and databases are not sufficient.
Types of Big Information
Structured, unstructured, and semi-structured data are all types of large data. Most of today's large data is unstructured, including videos, photos, webpages, and multimedia content. Each type of big data requires a different set of large data tools for storage and processing:
Structured data
Structured data is stored in an organized and fixed manner in the form of tables and columns. Relational databases are well-suited to shop structured data. Developers use the Structured Query Language (SQL) to process and retrieve structured data.
Hither is an instance of structured data, with lodge details of a few customers:
| OrderID | CustomerID | BillAmount | BillDate |
|---|---|---|---|
| ORD334567 | CUST00001234 | $250 | 17-04-2021 17:00:56 |
| ORD334568 | CUST00009856 | $300 | 17-04-2021 17:00:56 |
| ORD334569 | CUST00001234 | $100 | 17-04-2021 17:01:57 |
The Order table has a reference to the CustomerID field, which refers to the customer details stored in another table called Client.
Semi-structured information
Semi-structured data is structured but not rigid. Information technology is non in the form of tables and columns. Some examples are information from mobile applications, emails, logs, and IoT devices. JSON and XML are common formats for semi-structured data:
{ "customerID": "CUST0001234", "proper name" : "Ben Kinsley", "accost": { "street": "piccadilly", "zip" : "W1J9LL", "urban center" : "London", "state" : "England" }, "orders": [{ "orderid":"ORD334567", "billamount":"$250", "billdate":"17-04-2021 17:00:56" }, { "orderid":"ORD334569", "billamount":"$100", "billdate":"17-04-2021 17:01:57" }] } The information has a more than natural construction here and is easier to traverse. MongoDB is a good example of semi-structured data storage.
Multi-structured/unstructured data
Multi-structured data is raw and has varied formats. It can comprise sensor data, web logs, social media data, sound files, videos and images, documents, text files, binary data, and more. This information has no detail structure and hence is categorized every bit unstructured data. Examples include text files, sound files, and images.
It is difficult to shop and process unstructured data because of its varied formats. However, not-relational databases, such as MongoDB Atlas, tin easily store and process diverse formats of big data.
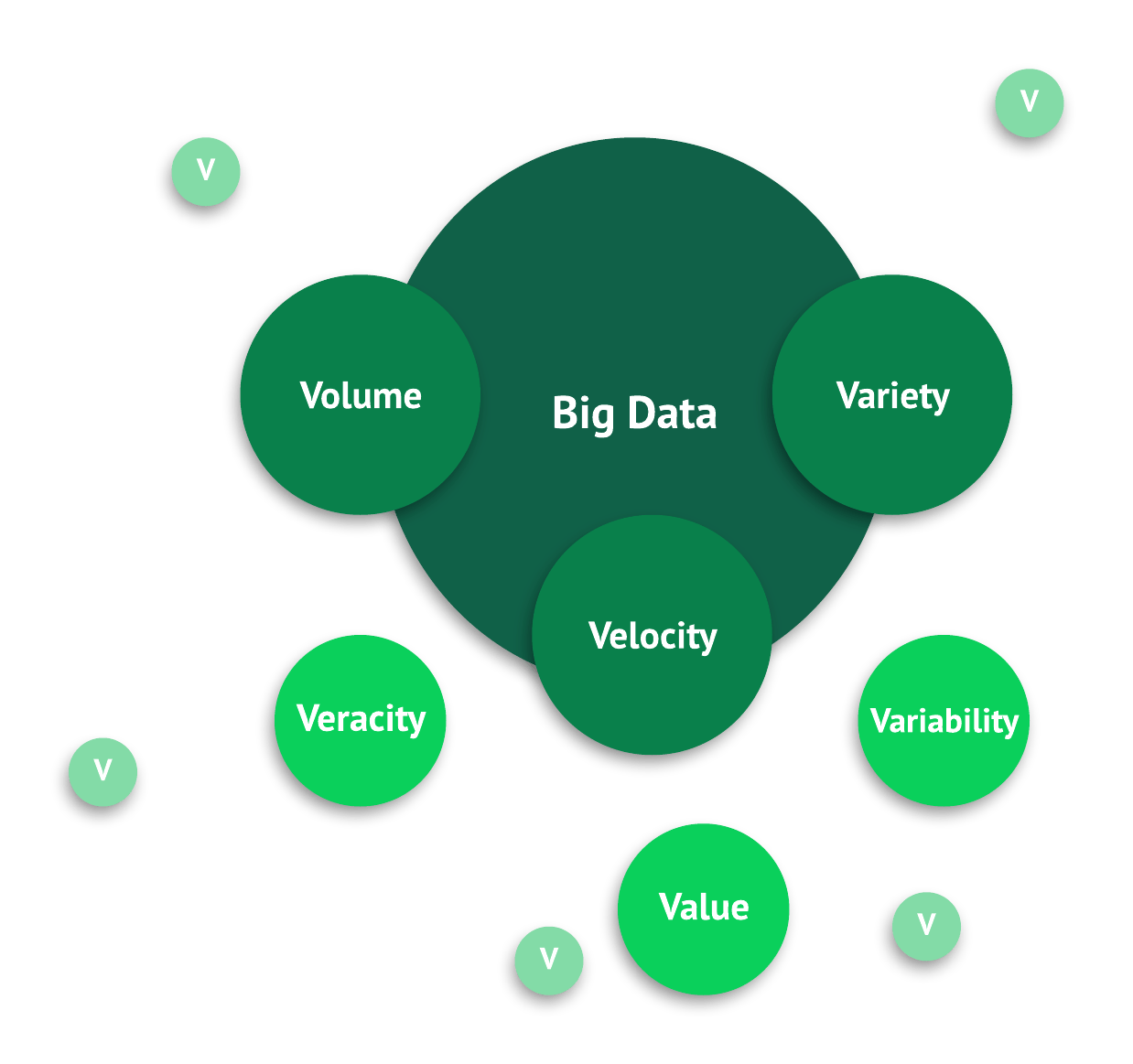
The Three Vs of Large Data
Big information has three distinguishing characteristics: Volume, Velocity, and Variety. These are known as the iii Vs of large data.
Volume
Data isn't "big" unless it comes in truly massive quantities. Just one cross-country airline trip can generate 240 terabytes of flight data. IoT sensors on a unmarried factory store floor can produce thousands of simultaneous information feeds every 24-hour interval. Other common examples of big data are Twitter information feeds, webpage clickstreams, and mobile apps.
Velocity
The tremendous volume of big data means it has to be candy at lightning-fast speed to yield insights in useful timeframes. Accordingly, stock-trading software is designed to log market changes within microseconds. Internet-enabled games serve millions of users simultaneously, each of them generating several actions every 2d. And IoT devices stream enormous quantities of consequence data in real time.
Variety
Large data comes in many forms, such as text, audio, video, geospatial, and 3D, none of which can be addressed by highly formatted traditional relational databases. These older systems were designed for smaller volumes of structured data and to run on merely a unmarried server, imposing real limitations on speed and chapters. Modern big data databases such as MongoDB are engineered to readily accommodate the need for diverseness—not just multiple data types, merely a broad range of enabling infrastructure, including scale-out storage architecture and concurrent processing environments.
Nowadays, more than Vs are making it to the definition of big data, the well-nigh prominent ones being:
- Veracity—the accuracy of big data.
- Value—the business concern value gained by analyzing the large information.
- Variability—the different data types and changes in the large data over time.
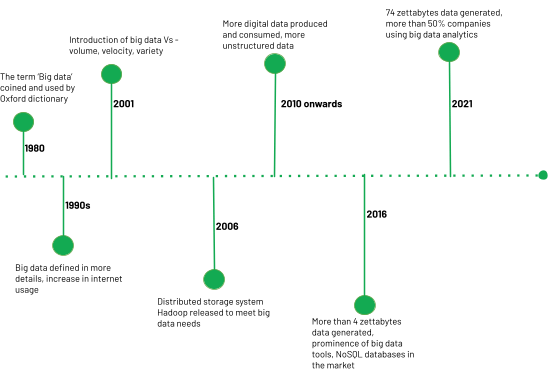
History of Big Data
Big data has come a long way since the term was coined in 1980 by sociologist Charles Tilly. Many researchers and experts anticipated an information explosion in the 21st century. In the late 1990s, analysts and researchers started talking more most what big data is and mentioning it in their research papers. In 2001, Douglas Laney, an industry analyst at Gartner, introduced the iii Vs in the definition of large data—volume, velocity, and multifariousness.
The twelvemonth 2006 was another milestone with the development of Hadoop, the distributed storage and processing arrangement. Since then, there have been constant improvements in the big data tools for analytics. Past 2016, the universe had already generated more than four zettabytes of information, and by 2021 it was estimated to be most 74 zettabytes (ane zettabyte = ane trillion gigabytes).
Large data analytics has become quite advanced today, with at least 53% of companies using large data to generate insights, save costs, and increase revenues. There are many players in the market and modern databases are evolving to become much amend insights from large data.
Why is Big Data Important?
Big data is used for gaining practical insights for procedure and revenue improvements. Large data assay tin assist in:
- Cost optimization: Through large data analytics, companies are able to amend their business organisation strategies, boost productivity by handling disasters before they occur, and focus more on the business concern rather than worrying about operational aspects, thus reducing overall toll.
- Innovative products and services: Through big information technologies, businesses are able to understand customer preferences better, and course their marketing strategies accordingly. This enables them to develop better products and services in time to come.
- Better, quicker decision-making: With the help of big data tools similar Spark, Hadoop, NoSQL databases similar MongoDB Atlas, visualization tools like MongoDB Charts, and others, analysts are able to become faster insights and big data solutions. This helps in quick decision-making for business.
How Big Data Works
To better empathize what big data is, we should know how big data works. Here is a simple big data example:
Defining Business Goal(s)
A clothing company XYZ wants to aggrandize its business by acquiring new users.
Data Collection and Integration
To do this:
- They need the assist of social media sites like Facebook, Instagram, Google, to understand user behavior—the posts users like, their engagement on particular pages, and so on.
- They create a website and track events on their website, including the number of clicks and minutes a user spends on a page.
- For the customers who browsed a particular section (similar women's ethnic wear), XYZ wants to send customized emails giving them offers and discounts.
- For queries and support, XYZ has chatbots and customer support bachelor.
All of this information cannot be nerveless from a single source. Each footstep has its own data center where the information goes. The information collected from various sources should be combined in one place to become a unified view. Such a place is normally referred to as a data lake or data warehouse. The process of collecting and combining data from various sources is called data integration.
Data Management
Next, XYZ has to store all the above data in a reliable and highly bachelor environment, where it tin be easily retrieved for business utilise. XYZ finds out that most companies adopt cloud-based storage and then that the infrastructure can exist easily managed. One such cloud-based data storage solution is MongoDB Atlas, which offers flexibility and scalability, among other features, and is also compatible with major deject providers like AWS, Azure, and more. Information tin exist hands updated and governed with big data deject storage.
The process of storing the integrated data, so that it can be retrieved past applications as required, is chosen data management.
Data Assay
In one case XYZ knows that the big data is managed well, the next stride is to figure out how the data should be put to use to become the maximum insights. The process of big information analytics involves transforming data, edifice machine learning and deep learning models, and visualizing information to become insights and communicate them to stakeholders. This pace is known as information analysis.
Let's summarize how big data works:
| Company XYZ big data example | Mapping to big information process | Proper noun of the big data analytics stage | Big information tools |
|---|---|---|---|
| XYZ wants to acquire new customers | Define business goals | Problem definition and understanding user needs: Why do we want to get for large data analytics? | Interviews, enquiry data, web logs, demographics, mobile information, emails |
| XYZ finds out multiple ways to ingest information | Know where data can exist sourced from and consolidate | Data collection, Ingestion and Integration from IoT, social media, deject, etc. | Kafka, NIFI, Kinesis, MongoDB data lake |
| XYZ finds out virtually cloud storage | Store big data, keep data updated | Data management | AWS, MS Chief Data Services, Talend, MongoDB Atlas, Google Cloud |
| XYZ hires data analysts and data scientists to become insights | Analyze large data | Data visualization and assay | Spark, SAS, MongoDB Charts, R, Python, Power BI |
Learn more than about MongoDB Data Lake, MongoDB Atlas, or MongoDB Charts.
This enables companies like XYZ to make information-driven decisions to create intelligent organizations. Big data is the fundamental to building a competitive, highly performant environment which can benefit businesses and customers alike.
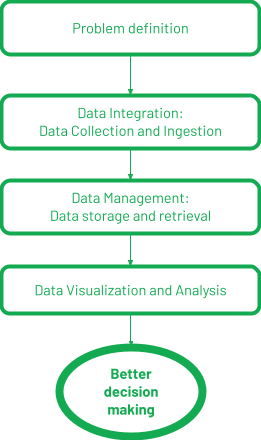
MongoDB can help at each phase of big data analytics with its host of tools similar MongoDB Atlas, MongoDB Information Lake, and MongoDB Charts.
MongoDB Atlas is a fully managed deject-based database service. Atlas takes care of complete database management, including security, reliability, optimal performance, and more, so that developers tin can focus on building the application logic.
Large Data Challenges
Collecting, storing, and processing big data comes with its own set of challenges:
- Big data is growing exponentially, and existing information management solutions take to be constantly updated to cope with the three Vs.
- Organizations do not have enough skilled information professionals who tin can sympathize and work with big data and big data tools
Learn more nigh the top seven big data challenges.
Big Data Examples and Use Cases
Before nosotros get into domain-specific large data examples, let'due south outset understand what big information is commonly used for.
What is large data used for?
Big data tin address a range of business organisation activities from customer feel to analytics. Here are some examples:
- Compliance and fraud protection: Big information lets yous identify usage patterns associated with fraud and parse through big quantities of information much faster, speeding and simplifying regulatory reporting.
- Machine learning: Large data is a key enabler for algorithms that teach machines and software how to acquire from their own experience, so they can perform faster, achieve higher precision, and discover new and unexpected insights.
- Product evolution: Companies analyze and model a range of big information inputs to forecast customer demand and make predictions as to what kinds of new products and attributes are most probable to adapt them.
- Predictive maintenance: Using sophisticated algorithms, manufacturers assess IoT sensor inputs and other large datasets to rail auto performance and uncover clues to imminent issues. The goal is determining the ideal intervals for preventive maintenance to optimize equipment operation and maximize uptime.
- Improving productivity and minimizing costs: To hone their border in depression-margin competitive markets, manufacturers utilise big data to better quality and output while minimizing scrap. Government agencies tin can employ social media to place and monitor outbreaks of infectious diseases. Retailers routinely fine-melody campaigns, inventory SKUs, and price points by monitoring spider web click rates that reveal otherwise hidden changes in consumer behavior.
Big Data Examples
Enterprises and consumers are producing information at an every bit high rate. The data tin can be used past several streaming and batch processing applications, predictive modeling, dynamic querying, machine learning, AI applications, and then on.
We touched upon big data applications in healthcare, marketing, and customer feel. Other common big data examples are:
- Fraud detection and prevention: By identifying suspicious transactions and activities, fiscal institutions can identify and differentiate frauds. Existent-time tracking and machine learning algorithms help in detection and prevention of cyber thefts, insurance scams, identity thefts, and many other online frauds.
- Recommendation systems: Apps like Netflix and Amazon Prime have now become the primary source of at-home amusement. These sites recommend programs that are like to the previous videos that they or other users liked. Amazon product recommendations work on the same principle.
Check out ix more existent-earth big information examples and employ cases.
How Does Big Data Work in MongoDB Atlas?
As nosotros have seen before, MongoDB has a document-based construction, which is a more natural way to shop unstructured data. Its flexible schema accepts data in any form and volume—so you don't have to worry about storage as the amount of data increases.
MongoDB Atlas is a secure, highly available, fully managed database-equally-a-service that is compatible with all the major cloud providers similar AWS, Microsoft Azure, and GCP. MongoDB Atlas is highly scalable, and has built-in tools similar charts for advanced big data analytics and insights. Atlas' information lake allows users to query for information in any format on the deject (currently supported for AWS).
Acquire more almost MongoDB Atlas.

Ready to acquire more?
Launch a new cluster or migrate to MongoDB Atlas with zero downtime.
FAQ
What is an example of big data?
What are big data tools?
What is big data and how is it used?
Where is big data stored?
How is big data collected?
What do you mean by large data?
Who is using big information?
What is big data, in uncomplicated terms?
What Is Some Information That Should Be Found In Big Data Databases?,
Source: https://www.mongodb.com/big-data-explained
Posted by: joneswattelf.blogspot.com


0 Response to "What Is Some Information That Should Be Found In Big Data Databases?"
Post a Comment